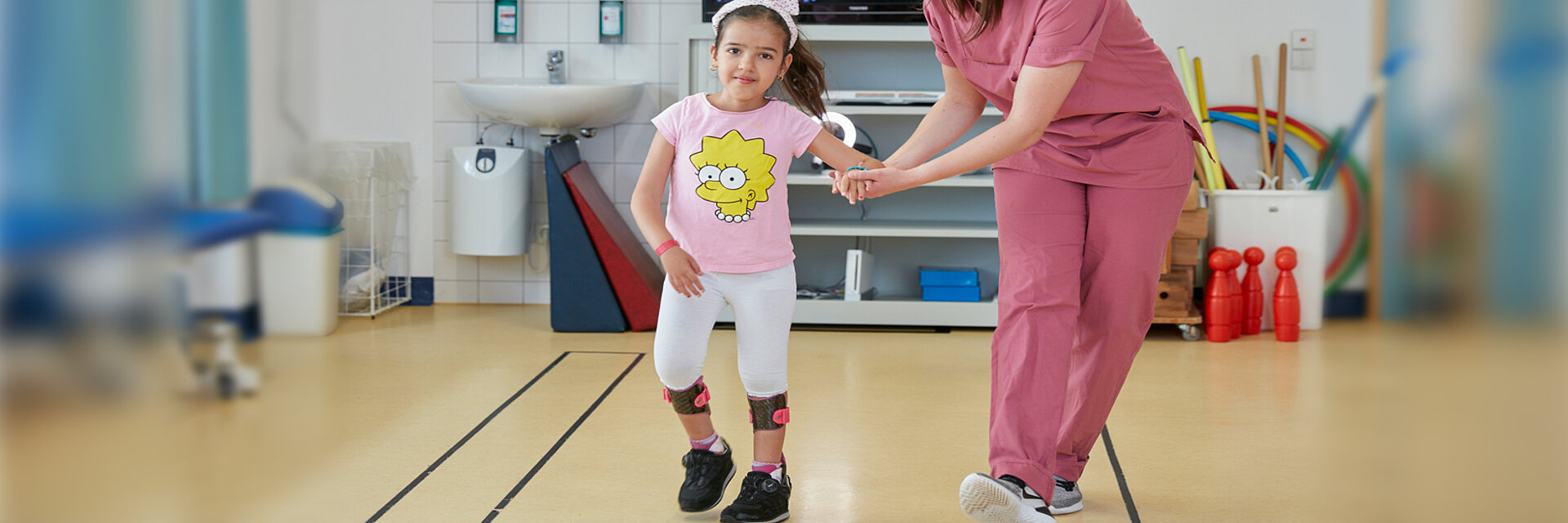
Cerebral Palsy
Birth complications can cause cerebral palsy
Cerebral palsy refers to a very variable clinical picture that can exist for many reasons. It must have developed before the first birthday, but the most common causes are prenatal or so-called peripartum, i.e. damage to the brain that occurred "around birth".
Cerebral palsy is named after the always existing partial paralysis or paresis, which can present itself clinically in different ways. A distinction is made between spastic, dystonic and ataxic cerebral palsies, and often there are mixed pictures. The classification of the degree of severity into five levels is usually done using the so-called GMFCS (Gross Motor Function Classification System).
The treatment of cerebral palsy is a multimodal developmental concept that includes functional therapies, the use of various medications, the provision of assistive devices, possible orthopaedic corrective surgery (see also neuroorthopaedics) and other individual measures. At the Children`s Hospital Schömberg, we carry out inpatient treatments that take all these aspects into account. The majority of our patients are so severely affected that they cannot walk freely. Often there are other medical reasons for treatment, for example epilepsy, behavioural problems or pain.

Drug treatment options
Several drug treatment options are available, especially for spasticity. In contrast, dystonia and ataxia can unfortunately only rarely be influenced favourably and sustainably with medication.
In addition, many medicines lack marketing authorisation in childhood. Nevertheless, in the absence of alternatives, an individual curative trial, which may be conducted under inpatient conditions, may be justified.
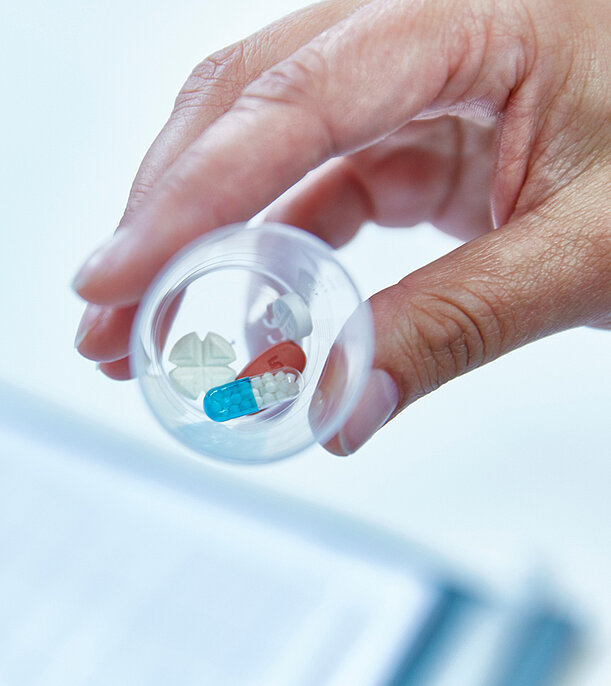

There are several drugs available in tablet form, so-called antispasticity drugs. Under in-patient treatment conditions, we can interdisciplinarily assess whether there is efficacy and where the effective dose lies.
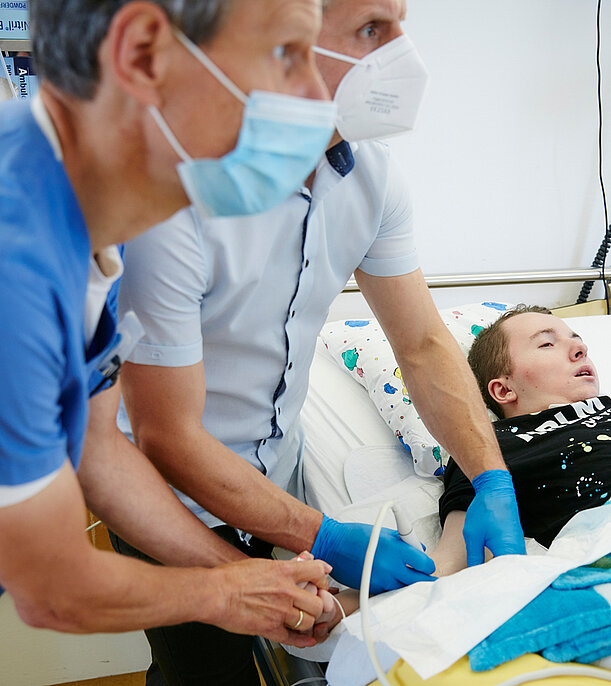
The injection of botulinum toxin into certain spastic or dystonic muscles has been carried out under sonographic control for years. Before deciding which muscles or muscle groups to treat with botulinum toxin, a thorough interdisciplinary assessment of the functional problems and their impact on participation is carried out.
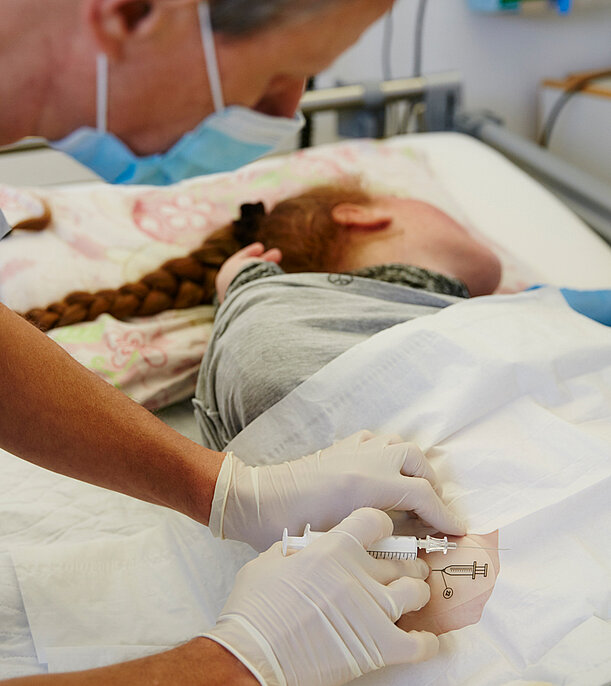
We are also happy to provide detailed advice on other options for spasticity and dystonia treatment if the conditions are right. If necessary, we will put you in touch with centres that offer therapy options such as the use of a Baclofen pump and deep brain stimulation (THS). However, THS is only a realistic therapy option for very few patients with very specific, narrowly circumscribed damaged areas of the brain.
We can readjust and refill existing baclofen pumps during the stay.




