Dysphagia treatment
Dysphagia - an underestimated problem
Dysphagia refers to a disturbed swallowing act and can occur both in isolation and in combination with other symptoms. The more severe a multiple disability is, the greater the risk that dysphagia is also present.
Mild forms lead to more frequent swallowing problems or to difficulties in taking in enough food and fluids in a reasonable period of time. This can already lead to underweight or even severe failure to thrive.
This can also lead to aspiration, i.e. the entry of saliva, pharyngeal secretions, drinks and food into the lower airways. The more severe and frequent this occurs, the higher the probability of (repeated) pneumonia. A weak cough increases this risk even more. As a result, oral feeding may not be possible, and in the most severe cases, the creation of a tracheostoma must even be considered.

Common focus on diagnostics
Targeted help for swallowing difficulties and disorders
If there is a suspicion of dysphagia, our medical team and our speech therapists carry out an exact assessment of the situation. If necessary, we can perform an endoscopic evaluation of the swallowing process (FEES) at our clinic. If the diagnosis is confirmed, our speech therapists will provide individual dysphagia therapy. In severe cases, we advise the patient's family about possible supportive or relieving measures.
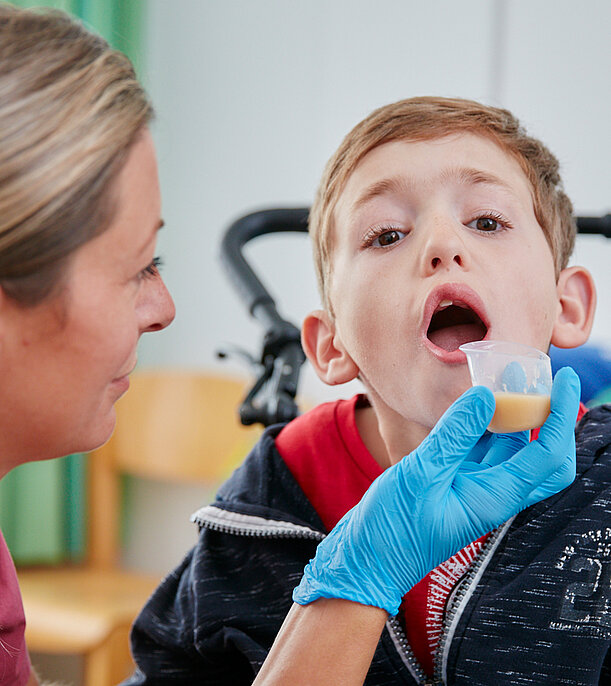
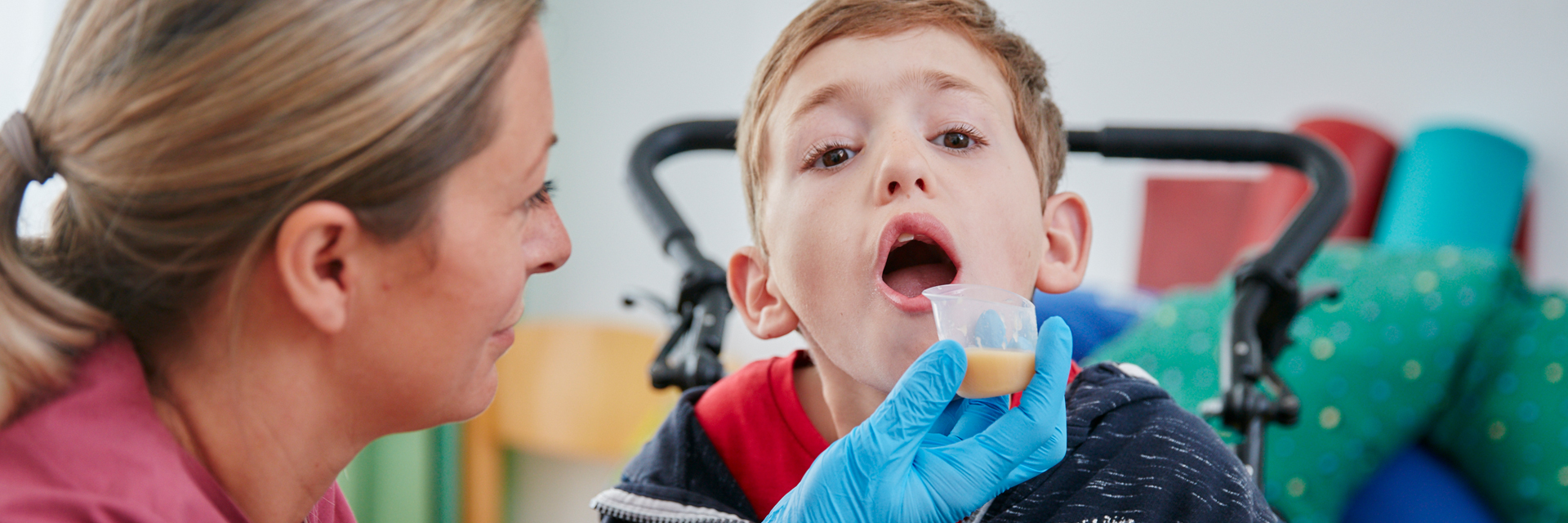
A doctor will assess whether there is a nutritional failure to thrive. For this purpose, a feeding protocol can also be kept for a few days. The observation of the feeding or eating situation by the speech therapist serves to differentiate other possible diagnoses such as feeding disorders. In most cases, we also carry out a clinical assessment of the swallowing cycle.
![[Translate to Englisch:] Endoskopische Schluckuntersuchung (FEES) Picture: During the endoscopic swallowing examination, a doctor uses an endoscope to examine the function of a boy's larynx.](/content/_processed_/c/3/csm_dysphagie-accordeon-1_a6950cdc84.jpg)
If the clinical assessment reveals a suspicion of aspiration, we perform an endoscopic swallowing examination (FEES). After the nasal mucosa has been treated with decongestant, a thin endoscope of a few millimetres is inserted through the nose into the throat. From there, the examiner has a good view of the larynx and can carry out tests on the function of the larynx if the patient cooperates. The act of swallowing can be assessed during the intake of food and liquid.
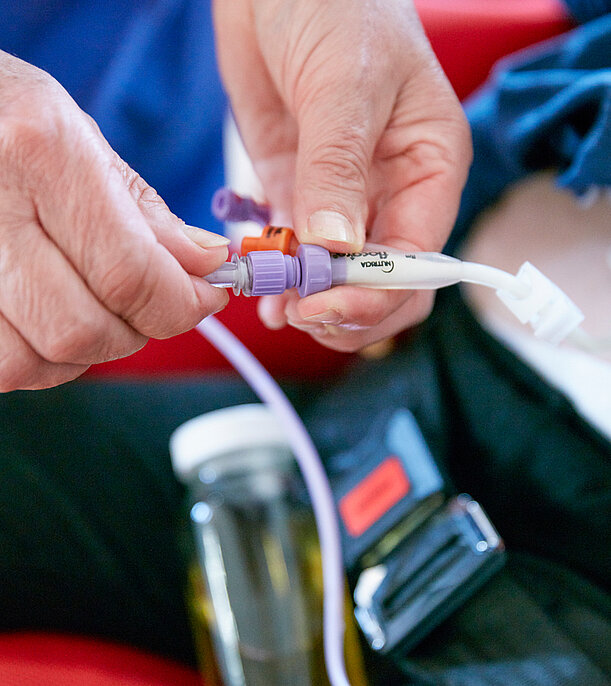
In serious cases, there is a need to advise relatives on how to ensure sufficient and safe nutrition. This is the case if inadequate purely oral nutrition impairs the child's growth. If severe complications such as choking or bronchopneumonia have already occurred, there is also an acute need for action.
If the feeding problems are only foreseeable for days to a few months, a nasogastric tube can be inserted to bridge the gap. This thin tube is inserted through the nose, throat and oesophagus into the stomach. If the problem is a chronic feeding problem, the insertion of a percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG or artificial gastric access) is indicated. If a PEG already exists, we discuss with the relatives whether and under what circumstances how much feeding is allowed.
Parents are often concerned that they will no longer be allowed to feed their child after a PEG insertion. However, this is rarely the case. The PEG tube opens up the possibility for the child not to have to eat all the time, but to be able to eat and drink as much as he or she wants with pleasure. Sometimes eating is successful in sufficient quantities and only drinking needs to be probed. If a PEG is inserted during the inpatient stay, this is done during a short transfer.



